Finite element analysis is a numerical technique used to predict the behavior of physical systems by dividing them into smaller, manageable elements. To harness the full potential of FEA, it is crucial to grasp the three fundamental stages that make up this analysis process: preprocessing, solution, and post-processing. Knowing the three stages provides students with a solid understanding of how to approach complex analysis and simulation tasks. For comprehensive learning, students can sign up for a finite element method course It will equip students with the ability to break down complex structures or systems into simpler elements for analysis, a fundamental skill in engineering and scientific disciplines.
Many industries, including aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and biomechanics, rely heavily on FEA for design and analysis. Students who understand the three stages are better equipped for careers in these industries. In this blog, we will explain these stages in a detailed manner.
Understanding the Three Stages of Finite Element Analysis
Let us explore the three main stages of FEA in detail:
Preprocessing
When you enroll in a finite element method course, this is the first step that you will learn about. Here is what happens in the preprocessing stage:
Geometry & Mesh Generation: In this stage, the physical geometry of the system is defined by importing a computer-aided design model or developing it directly within the analysis software. Then, the domain is discretised into a mesh, which is a collection of small finite elements that approximate the geometry of the system.
Material Properties: During pre-processing, the material properties of the units within the system are specified. These properties include parameters like density, thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, etc. It is essential to accurately define these properties, as they significantly influence the behavior of the system under different loading conditions.
Boundary Conditions: Boundary conditions are conditions that are applied to the system to define how it connects with its external forces or environment. This includes constraints and loads. Properly defining boundary conditions is critical for obtaining accurate and meaningful results.
Element Types: The choice of element types is crucial in accurately representing the geometry and physical behavior of the system. Different types of components can be used based on the nature of the problem.
Solution
This is where the mathematical equations governing the behavior of the system are solved. There are different types of analyses, including:
Equation Assembly: In this stage, the equations that govern the behavior of the system are assembled based on finite element discretisation. The equations that are associated with individual elements are then combined to create a global system of equations that represents the entire system.
Numerical Solution: A lot of numerical techniques are used for solving the system of equations. This can involve direct solvers or iterative techniques. The numerical solution yields values for the unknowns within the system, which include stress, deformation, frequency, etc. These values provide detailed information about how the system responds to the specified conditions.
Did you know, at Niharika Institute of Computational Engineering, we provide the best
Post-processing
After the analysis is complete, the results need to be interpreted and visualized. This is where the postprocessing stage comes into play.
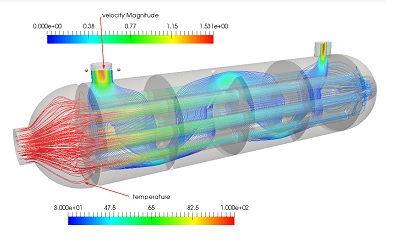
Visualization: The results obtained from the solution stage are visualized to help in understanding the behavior of the system. This typically includes generating contour plots to depict various parameters, animations to show deformations, or maps illustrating stress distributions.
Quantitative Analysis: Quantities of interest, such as heat fluxes, displacements, or maximum stresses, are extracted and examined to find out the performance of the system.
Sensitivity Analysis & Optimization: Post-processing also involves sensitivity optimization or analysis techniques. These methods help understand the effects of various design parameters as well as optimize the performance of the system based on certain objectives. This can lead to improvements in the design and efficiency of the system.
Final Thoughts
FEA is used in various disciplines beyond traditional engineering fields, such as medical modeling, geophysics, and environmental science. Knowing the stages of FEA expands the range of applications students can explore. It also allows students to focus on the most critical aspects of the analysis, ensuring time and computational resources are utilized efficiently. So, should you want to learn finite element analysis, join Niharika Institute of Computational Engineering. We provide the best finite element method course to help students solve real-world engineering problems by providing them with a powerful computational tool.